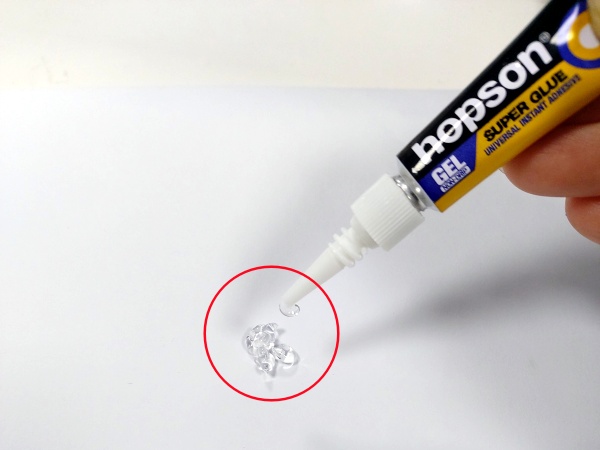
Glue is useful for many things, such as making crafts, woodworking, and industrial goods. The viscosity and strength of glue are two important factors that affect how useful it is in different situations. Understanding these characteristics can help you choose the right adhesive for your specific needs.

What is Glue Viscosity?
Viscosity is a measure of how easily glue flows. The higher the viscosity, the thicker the glue, and the worse it flows; the lower the viscosity, the thinner the glue, and the better it flows.
For example, water has a low viscosity, and honey has a high viscosity. When you use thin glue on smooth surfaces, it spreads quickly. When you use thick glue on vertical or porous materials, it stays in place.
The right viscosity ensures the application is correct and the bond is strong. Temperature also changes viscosity; heat makes glue thinner, and cold makes it thicker.
What is Glue Strength?
Adhesive bond strength is a key quality indicator for adhesives. It refers to the ability of the glue and substrate interface (or adjacent area) to resist external force damage. The glue strength is often measured by its ability to resist forces like tension, shear, or compression.
Based on real-world stress conditions, bond strength is further categorized into:
- Shear strength (resistance to sliding forces)
- Tensile strength (resistance to pulling apart)
- Peel strength (resistance to layer separation)
- Impact strength (resistance to sudden shocks)
A stronger glue will be more resistant to being pulled apart or broken under stress.
The actual bond strength depends on multiple factors:
- Adhesive properties (chemical formulation, mechanical performance)
- Substrate materials
- Bonding techniques
- Joint design
- Force conditions (type, magnitude, direction, frequency)
- Environmental factors (temperature, humidity, pressure, chemical exposure)
- Testing methods and measurement accuracy
Viscosity and strength are two important performance indicators of glue, but there is no direct relationship between the two. When selecting glue, it is necessary to comprehensively consider these two indicators based on specific needs to ensure that the glue can both meet construction requirements and provide sufficient bonding strength.
How to choose the right glue?
There are so many types of glue to choose from; selecting the perfect glue requires understanding your specific needs.. First, have a look at:
1. Your materials:
- Use medium-viscosity or high-viscosity glues (such as white wood glue, polyurethane wood glue, or super glue gel for wood) on porous materials like wood, since they soak up thin glues too rapidly.



- For bonding smooth metals/glass, you need low-viscosity cyanoacrylate to penetrate microscopic pores.
- Flexible materials (rubber/vinyl) require elastic adhesives like silicone.


2. Needs for Performance:
- Quick fixes? Super glue dries in a matter of seconds.
- Loads that are heavy? Two-part epoxy makes bonds that are strong enough for industry.
- Gap filling? Thick gel formulas bridge up to 5 mm spaces.
Note: The right glue combines proper viscosity for application with adequate strength for long-term performance.
For Special Uses
When normal adhesives can’t meet unique requirements, Hopson Adhesives delivers customized bonding solutions. With over 17 years of expertise in adhesive formulation, our engineers develop specialized products for the following applications:
- Bonding materials that are hard to bind, like silicone and EDPM.
- Chemical and waterproof uses.
- Biocompatible bonding that meets medical standards.
- Industrial settings with a lot of vibration.
As a glue adhesive manufacturer with in-house R&D labs, we can change the viscosity, curing time, and strength to fit your unique needs, whether you need to fix large equipment or delicate electronics assembly.

FAQ
How to Test Glue Bond Strength?
With hundreds of adhesive types available, from super glues to industrial epoxies, their bond strength varies dramatically. Choosing the wrong adhesive without proper testing can lead to product failures, safety hazards, and costly repairs.
To ensure reliable performance, it’s important to understand how to measure the bonding strength of glue. Here are five major methods used to test glue strength:
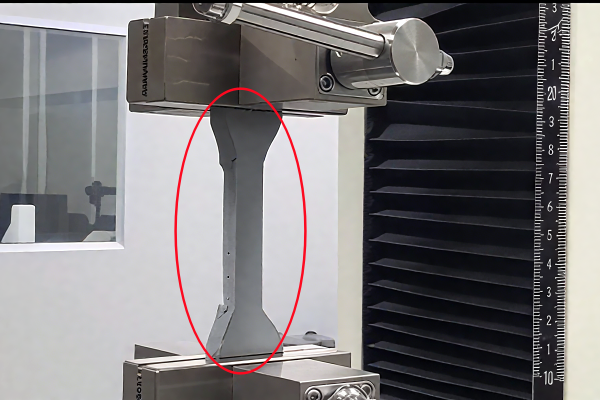
1. Tensile Strength Test
Apply tensile force in the vertical direction along the bonding surface, measure the maximum stress at failure, to evaluate the tensile performance of the adhesive in the vertical direction. Such as structural adhesives, metal bonding, etc.
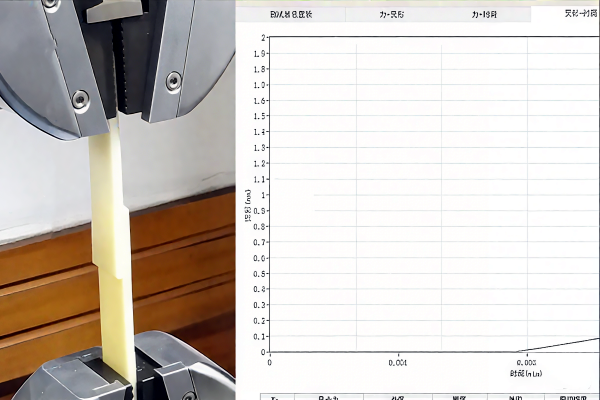
2. Shear Strength Test
Apply a force parallel to the bonding surface, and through single lap shear or double lap shear tests, record the failure stress to evaluate the strength of planar bonding in metals, plastics, composites, etc.
3. Peel Strength Test
Measure the force required to peel the adhesive layer from the substrate at a specific angle (e.g., 180°), record the peel force curve, and test the adhesive performance of the glue on flexible materials.
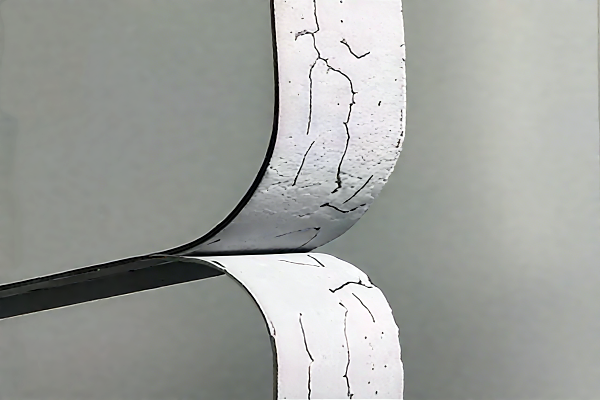
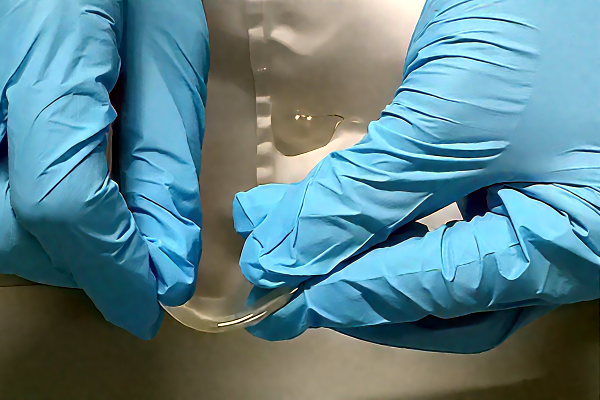


4. Environmental Aging Test
Simulate humidity and heat, temperature cycling, UV aging, or strength variations in chemical environments to test the durability of adhesives under complex conditions.
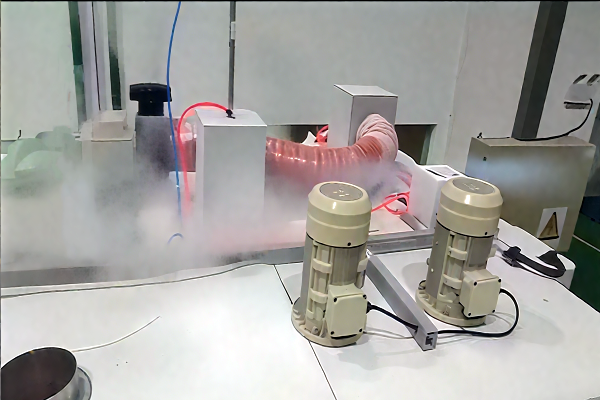
5. Impact Strength Test
Through pendulum impact or drop ball tests, measure the energy absorbed by the bonded joint upon fracture to evaluate the toughness of the adhesive under dynamic loading. Applicable to the impact resistance performance of automobiles and electronic devices.
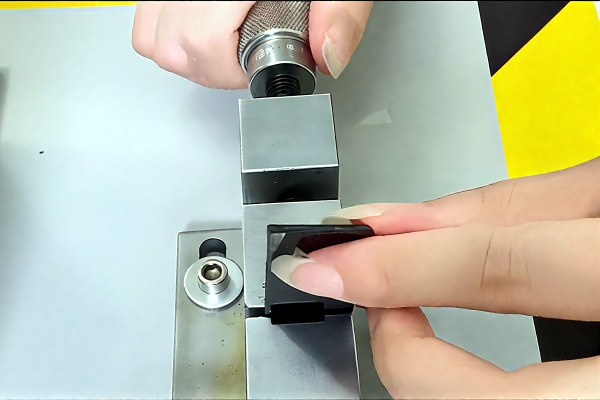
What is the difference between initial curing and complete curing of glue?
Initial curing refers to the adhesive reaching approximately 25% of its curing strength. At this point, the adhesive already possesses a certain degree of bonding strength, allowing for the next process step or the ability to withstand some pressure.
However, it will still be tacky and may become soft, and the bonding strength has not yet reached its maximum state.
In contrast, full curing refers to the glue reaching its final curing strength, at which point the glue no longer feels sticky, the surface becomes hard, and the bonding strength reaches its maximum, allowing for long-term stable adhesion.
How to Quickly Get the Right Bonding Solution for Your Project?
To provide the most suitable adhesive recommendation, we need the following key details about your application:
1. Materials to Be Bonded
- Base materials (e.g., PC, PVC, TPE, TPU, EVA, metal, ceramic)
- Material properties (porous/non-porous, flexible/rigid)
- Surface shape (flat, curved, textured)
- Bonding area size
2. Adhesive Requirements
- Curing speed (instant/fast/slow)
- Application method (dispensing, brushing, spraying)
- Special properties needed (conductive, thermal, flexible, etc.)
3. Application Environment
- Industry use (medical, electronics, automotive, etc.)
- Operating conditions (temperature range, chemical exposure)
- Stress types (peel, shear, impact, vibration)
4. Testing Standards
- Environmental tests (85°C/85% RH, thermal cycling, etc.)
- Chemical resistance (solvents, oils, acids)
- Industry certifications (ISO, Reach)
Pro Tip: The more details you provide (even photos help, the faster we can:
- Narrow down suitable adhesive types
- Suggest optimal application methods
- Ensure your product meets all performance requirements
How to test if the glue's performance is stable?
- Sampling and curing: Extract samples from each batch and cure them into standard-sized hardness blocks.
- Hardness testing:
• Use a durometer (Shore durometer) to test 3-5 samples per batch.
• Record the average hardness value - Comparative analysis: Compare the hardness values of different batches to assess whether the performance is stable.
Mark values with changes exceeding 10% as outliers.
How should different types of glue be properly stored?
The performance of glue is closely related to storage conditions; improper storage can lead to curing failure, viscosity changes, or strength reduction. Here are the storage tips for common adhesives:
Instant adhesive (cyanoacrylate)
- Storage temperature: It is recommended to refrigerate unopened at 2-8℃ (such as in a household refrigerator), with a shelf life of 1-2 years.
- After opening, it must be sealed, stored in a cool place (below 25℃) away from light, and protected from moisture to prevent failure.
- After taking it out of the refrigerator, it needs to be brought back to room temperature (about 2 hours) before opening the lid to prevent condensation from mixing in.
Anaerobic adhesive
- Storage conditions: Store in a cool, dark place at room temperature (10-28°C), humidity ≤50%.
- Must use polyethylene containers (metal/glass bottles are not allowed), and only fill them 2/3 full to avoid polymerization deterioration caused by air exclusion.
- Use it as soon as possible after opening (within 1-2 weeks), otherwise, its performance will decline.
UV glue (light-curing adhesive)
- Storage environment: Avoid light (especially ultraviolet), keep dry, temperature 5-25℃.
- Unused glue must be stored separately and not returned to the original packaging.
- Expired or discarded glue must be treated as hazardous waste.
- Storage method: Ventilated, dry, cool room temperature (20-25℃), shelf life 12 months.
- Avoid contact with acids, bases, and solvents.
- Temperature/Humidity: 5-25℃, humidity ≤50%, avoid temperature fluctuations, shelf life 12 months.
- It needs to be kept in the dark and sealed to prevent the isocyanate groups from reacting with moisture.
Hot melt adhesive
- Storage conditions: Store in a cool, dark place, at room temperature (10-22°C), shelf life 18-24 months
White latex (polyvinyl acetate) glue
- Temperature range: 5-30℃, freeze and high-temperature resistant, store in glass/plastic containers
Note:
- Sealing: All adhesives must be strictly sealed to prevent air and moisture from entering.
- Classification storage: Store different types of rubber separately to avoid cross-contamination.
- Regular inspection: Observe changes in color and viscosity, and discontinue use if abnormalities are detected.








